Serbian producers exporting duty-free to the EU since 2000
Customs duties for all industrial and agricultural products coming from Serbia into the EU (aside from only a few agricultural products protected by the preferential tariff quotas) were abolished by the EU in 2000 with the application of the Autonomous Trade Measures. This regime was unilaterally granted by the EU to Serbia in 2000 and it represented the most extensive trade concessions regime that was ever granted by the EU to any country or group of countries. This meant that the EU had immediately abolished all customs duties and quantitative restrictions on imports of all industrial and agricultural products, aside from only a few agricultural products that are under the preferential tariff quota regime (sugar, baby beef, wine and a few types of fish).
Serbia gradually removing customs protection since 2009
For Serbia, the reduction of import duties for goods originating in the EU started nine years later in January 2009 when Serbia voluntarily initiated the implementation of the trade-related part of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement, called the Interim Agreement. This agreement introduced asymmetric trade liberalisation in favour of Serbia for both industrial and agricultural products. In other words, since 2009, trade liberalisation on the Serbian side has been following a gradual and predictable six years’ liberalisation schedule, reflecting the level of sensitivity of products for Serbian producers. At the same time, a level playing field was being gradually introduced through the implementation of a predictable customs regime, anti-trust, state aid rules as well as the intellectual and industrial property protection regime in Serbia. This gradual trade liberalisation schedule was supposed to enable Serbian producers to progressively prepare for growing competition from the EU.
From January 1, 2014, Serbia and the EU have reached the sixth and final year of the trade liberalisation schedule. However, the most sensitive agricultural products for Serbian farmers will remain protected with customs duties until Serbia’s accession to the EU, notably all kinds of meat, yoghurt, butter, certain types of cheese, honey, certain vegetables and flour, with their tariff protection ranging from 20% to 50% of the most favoured nation (MFN) duty that Serbia applies to the rest of the world.
Entry into force of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement
The entry into force of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement in September 2013 further reinforced economic benefits of the Interim Agreement. A number of new provisions contributed to improving the business environment in Serbia, including provisions related to the free movement of capital, public procurement, standardisation, rights of establishment and supply of services. These policy changes provide a clearer and safer framework for investors and businesses, thus creating new momentum for the Serbian economy in attracting investments and improving the level playing field. Implementation of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement is supposed to raise standards of doing business for Serbian companies, gradually preparing them to compete with the EU companies on the Single Market and increasing their competitiveness in the long run.
For Serbian citizens, this should generate more variety of choice and decrease the prices of goods. Finally, the gradual opening of the market for public tenders to EU companies should result in more competition in public procurement procedures and is supposed to consequently bring better value for money to Serbian tax payers – better public works, supplies and services with less tax payers’ money.
Benefits from Serbia – EU trade
Serbia has substantially benefited from trade and economic integration with the EU. The EU is traditionally Serbia’s key trading partner accounting for nearly 65% of Serbia’s total exports and around 64% of Serbia’s total imports of goods in 2019, with similar percentages persisting over the years. The value of Serbian exports to the EU more than tripled from nearly EUR 3.4 billion in 2009 to almost EUR 11.3 billion in 2019!
Serbia’s exports to the EU have been growing faster than imports from the EU. Furthermore, the coverage of imports by exports on the Serbian side vis-à-vis the EU has been improving; from below 50% in 2009 to over 74% in 2019 (74.3% of imports from the EU were covered by Serbian exports to the EU).
Individual EUMSs traditionally top the list of Serbia’s most important trade partners in goods, notably Italy and Germany, but also Romania as an important export destination and Hungary as important country of origin for Serbian imports. Serbia exported almost 19% of total exports to Italy alone and another 15.1% to Germany in 2019. On the import side, Serbia imported more than 22% of all imports from Germany, with Italy following at 14.9%.
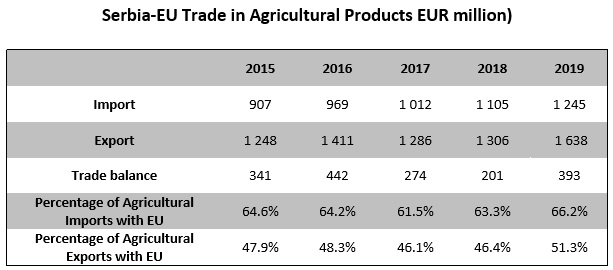
Concerning trade in agricultural and food products, Serbia enjoys a surplus vis-à-vis the EU. The surplus reached its peak in 2016 at more than EUR 440 million. In 2019, trade in agricultural and food products again picked up, in comparison to 2018, with the surplus increasing to EUR 393 million.
The significance of the EU market as an export destination for Serbian agricultural products is considerable, as more than half of Serbia’s agricultural exports are shipped to the EU. In 2019, Serbian agricultural exports to the EU accounted for 51.3% of total agricultural exports. Serbia’s agricultural exports to the EU more than doubled over the past decade, steadily rising from EUR 640 million in 2009 to over EUR 1.6 billion in 2019. At the same time, Serbian imports of agricultural products from the EU increased from EUR 440 million in 2009 to over EUR 1.2 billion in 2019.
Investment benefits for Serbia
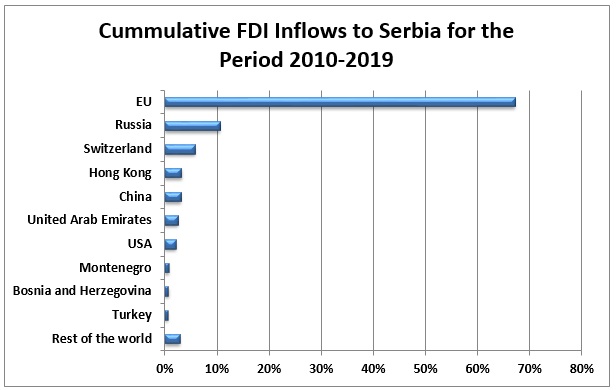
Foreign direct investment coming from the EU accounted for almost 70% of total FDI coming to Serbia over the past ten years, from 2010 until 2019. In absolute terms, FDI from the EU countries reached over EUR 15 billion for the past ten years.
Companies from the EU have been the leading investors in Serbia over the previous decade. These companies have brought efficiency, modern technology and know-how into the Serbian economy. This has in turn significantly increased productivity and competitiveness of the Serbian economy, boosting its export potential, increasing budget revenues and generating economic growth. Ultimately, opening up of the Serbian market to companies from the EU has generated a variety of choice and lower prices for consumers.
Exports from Serbia
- The value of exports to the EU accounts for nearly 65% of total Serbian exports in 2019, with a steady increase over the past years.
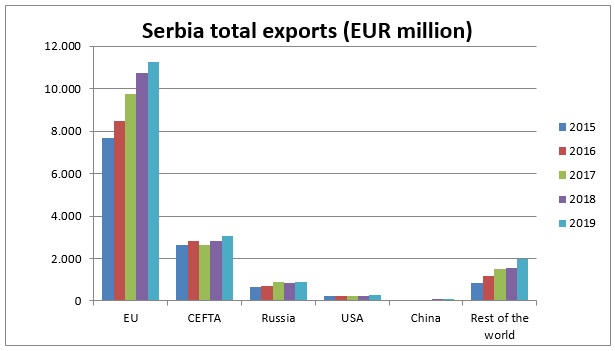
Source: Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia and Eurostat Comext – Statistical regime 4
Imports to Serbia
- More than 63% of all imports arriving to Serbia come from the EU.
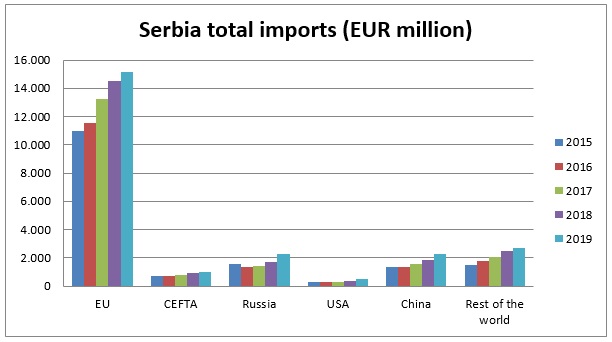
Source: Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia and Eurostat Comext – Statistical regime 4
Serbia-EU Trade
- Total Serbia-EU trade volume is steadily increasing
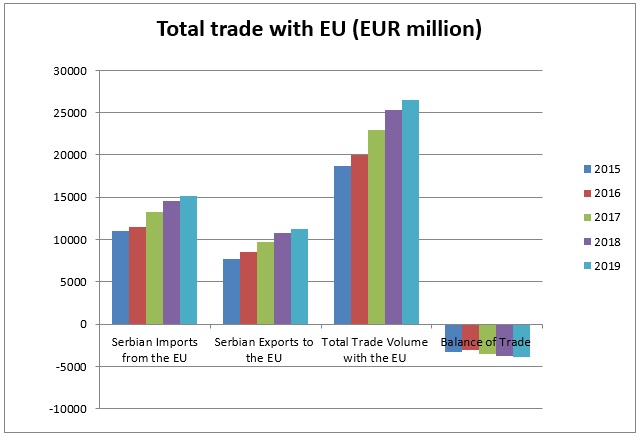
Source: Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia and Eurostat Comext – Statistical regime 4
Serbia-EU Trade in Agricultural Products
- Serbia enjoys a surplus in agricultural trade vis-a-vis the EU.
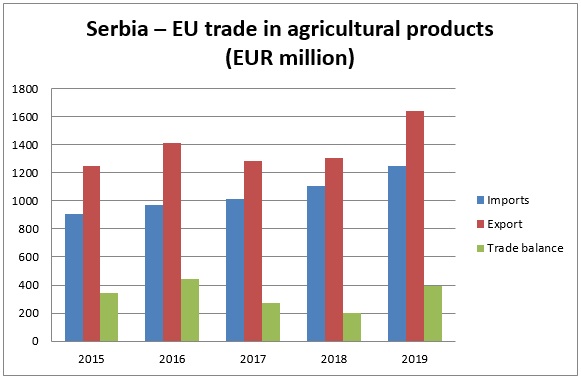
Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Water Management of the Republic of Serbia
FDIs to Serbia
- EU companies invested almost 70% of the cumulative FDI inflows to Serbia over the past ten years – amounting to over EUR 15 billion in total!
Source: National Bank of Serbia
Access2Markets – Your EU Gateway to trade information
What is it?
Access2Markets is an online information portal with all you need to know about EU trade agreements, duties, product rules and customs formalities for the EU and for over 120 markets around the world.
Access2Markets is the portal for EU where you can find detailed information on:
- tariffs
- rules of origin
- product requirements
- customs procedures and formalities
- VAT/excise duties/sales taxes
- Trade barriers
- trade statistics
Who is it for?
Access2Markets is for companies, business organisations, chambers of commerce, business advisory services such as the Enterprise Europe Network, for Export Promotion Organisations and all other entities who work with and advise companies in exploring export opportunities or where to source goods from outside the EU.
How does it work?
The portal offers a single search window for import and export to look up life data for the to-date applying trade conditions for each product, each trade agreement and arrangement. This product-specific information includes customs formalities, product legislation, the contact details of competent authorities in every country. The portal comes in all 24 official EU languages.








